Photosynthesis is one of the most fundamental processes on Earth, fueling not only the growth of plants but also the entire food chain, including humans. As a scientist with a passion for biology and chemistry, I’m fascinated by the elegant chemistry that underlies this process — and I’d like to share how it works and why it matters.
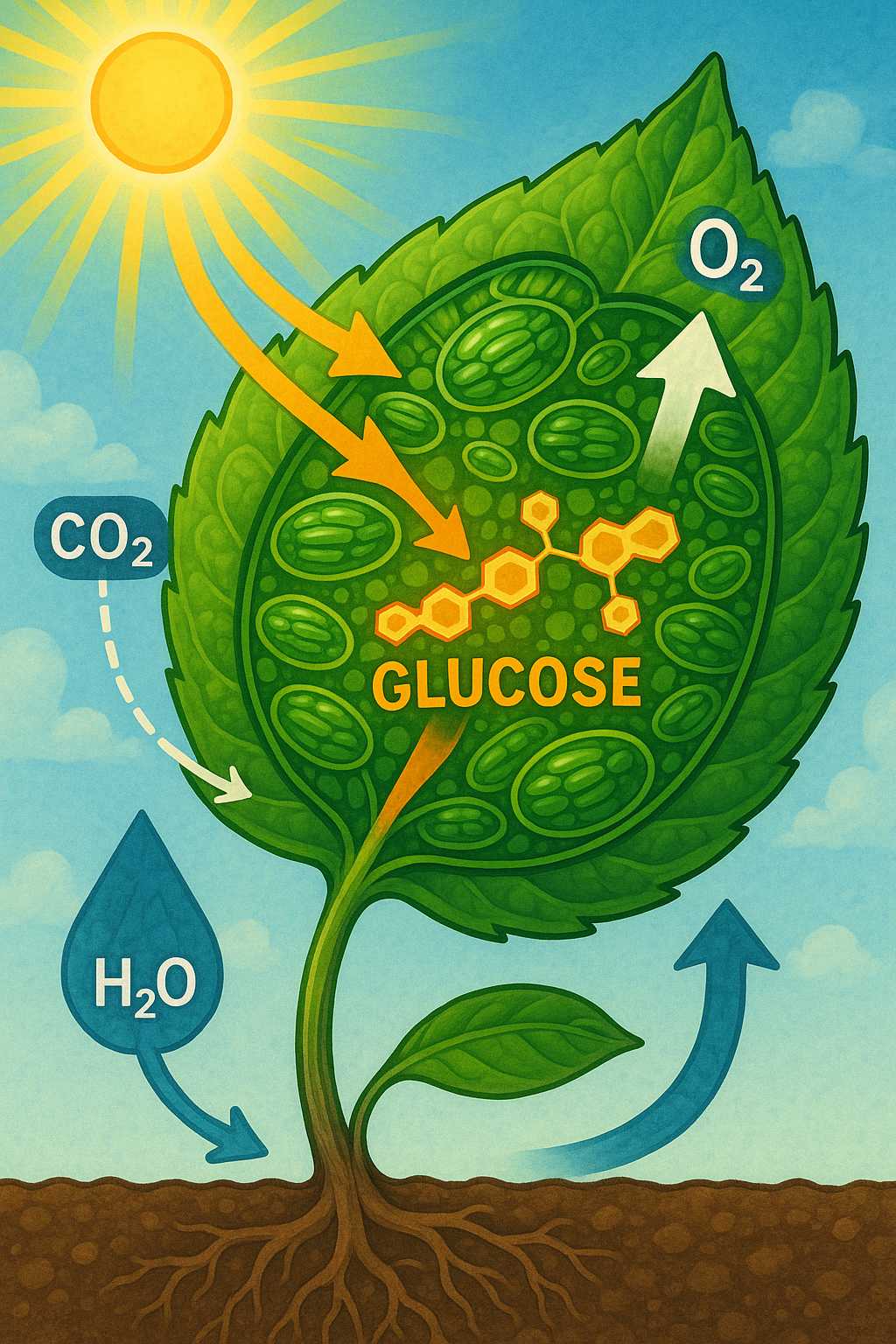
At its core, photosynthesis allows plants to convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of sugars, which they use to grow. This process takes place inside special cell structures called chloroplasts, which contain a green pigment known as chlorophyll. Chlorophyll captures sunlight, initiating a series of chemical reactions that split water molecules (H₂O) into hydrogen and oxygen.
The hydrogen, combined with carbon dioxide (CO₂) taken in from the air, is used to synthesize glucose (a simple sugar). Oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct. The overall simplified equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
What makes photosynthesis truly remarkable is its efficiency and impact. Not only does it provide the organic compounds essential for plant life, but it also produces the very oxygen we breathe. Moreover, the sugars generated by this process serve as the foundation for nearly every food web on the planet.
Understanding photosynthesis is also crucial in the fight against climate change. Plants act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO₂ and helping to regulate the Earth’s atmosphere. Scientists are even studying ways to mimic photosynthesis artificially, aiming to create sustainable energy solutions.
In summary, photosynthesis is much more than a science lesson from school — it’s a sophisticated, natural process that sustains life and shapes our world. Next time you see a patch of green, remember the microscopic magic happening within each leaf!

Leave a Reply